The Functioning Urea Cycle

Urea Cycle Disorders (UCDs) are a group of rare inherited metabolic diseases characterized by deficiencies of one of the enzymes and transporters involved in the urea cycle.
The urea cycle is necessary for the removal of nitrogen produced from the breakdown of protein. UCDs are characterized by hyperammonemia and life-threatening hyperammonemic crises.1
The treatment of UCDs may include an ammonia scavenger treatment as well as dietary protein restriction and dietary supplements.
Mechanism of Action

Two ammonia scavengers are approved as a chronic UCD treatment by the US Food & Drug Administration (FDA) – GPB (glycerol phenylbutyrate) and NaPB (sodium phenylbutyrate).3,4 The glycerol and the sodium are essentially the delivery mechanisms for the phenylbutyrate (PB).
Both of these FDA-approved nitrogen scavengers for chronic UCD management contain Phenylbutyrate (PB), a prodrug of phenylacetate (PAA), which conjugates glutamine to form phenylacetylglutamine (PAGN) for urinary excretion by the kidneys.2,5
For each mole of PAA, 2 moles of ammonia are eliminated in the urine.6
Adapted from Misel et al, 2013 and Ficicoglu et al, 2022
The mechanism of action for all forms of phenylbutyrate (glycerol and sodium) results in the same outcome: For each mole of PAA, 2 moles of ammonia are eliminated in the urine.2,6-7
PHEBURANE® COATED PELLETS:
An innovative formulation of sodium phenylbutyrate (NaPB) with a special coating designed to mask the awful taste
P=PALATABLE
P=PELLETS
Pheburane® pellets are small and round with sugar cores, a layer of NaPB – the active ingredient, and a coating of ethyl cellulose, a well-known taste-masking agent.5
Pheburane® should be combined with dietary protein restriction and, in some cases, amino acid supplementation (e.g. essential amino acids, arginine, citrulline, and protein-free calcium supplements).
Consider Pheburane® for your appropriate naïve to treatment patients. Start your patients on Pheburane® to give them the benefit of a taste-masked version of NaPB.
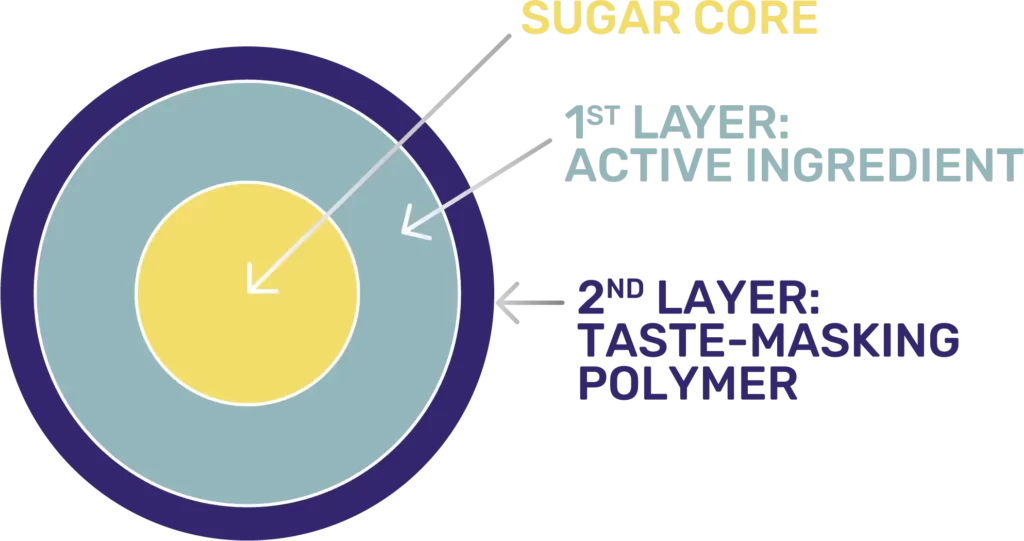

10 Second Window of Opportunity
The in vitro test profile of Pheburane® coated pellets indicates that the NaPB was only released after approximately 10 seconds followed by a slow release over several minutes. Therefore, patients must take as directed and optimally within 10 seconds to avoid any bad taste.4
Consider switching your appropriate patients to Pheburane® - a PALATABLE, FDA APPROVED SAFE & EFFECTIVE treatment alternative.
If your patients are currently taking another ammonia-scavenging medication, switching your patients to Pheburane® may provide a palatable alternative at a cost that is similar to other NaPB products and significantly less expensive than the most commonly prescribed chronic UCD treatment.
Dosing*
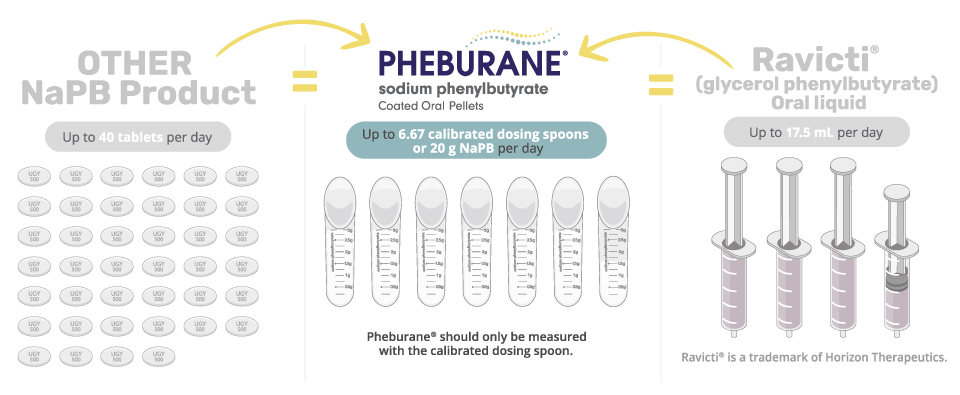

*Depiction of maximum daily dosing regimen for patients switching from other products to Pheburane ®. Tablets, dosing spoons, and oral syringes are not shown to size.
Switching from another NaPB Product to Pheburane®1
If switching a patient from another NaPB formulation (such as powder/granule/pellet) to Pheburane® the daily dose remains the same. Patients can immediately begin taking Pheburane® by measuring the same daily dose with the calibrated dosing spoon provided.
If switching a patient from NaPB tablets, and the patient is currently taking 500 mg tablets, the Pheburane® daily dosage would be equivalents to half the number of tablets previously taken (i.e., 40 tablets per day would equal a daily Pheburane ® dosage of 20 g).
Switching from Ravicti®* to Pheburane®2,3
If switching a patient from Ravicti® to Pheburane®, the patient’s daily dose will change. Either calculate the Pheburane® daily dose of NaPB based on weight/body surface area of the patient by using the below Dosing Calculator.
OR
Use this Conversion: Current Ravicti® (glycerol phenylbutyrate) total daily dose (mL) x 1.165 = Total daily NaPB dose in grams.
How to Calculate Pheburane® Dosage
Recommended oral dosage (measured as sodium phenylbutyrate or NaPB):
- Patients weighing < 20 kg: 450-600 mg/kg/day
- Patients weighing ≥ 20 kg: 9.9 – 13 g/m2/day
Dose must be measured using only the reusable calibrated dosing spoon. The calculated total daily dose of Pheburane® should be divided into 3 – 6 equal amounts and taken with food consumption (meal or snack). Maximum daily dosage is 20 g per day.
- Monitor plasma ammonia levels to determine need for dosage adjustment.
- Monitor patients for potential neurotoxicity.
- For patients with hepatic impairment, start at the lower end of the recommended dosing range.
Dosing calculator
For patients weighing less than 20 kg (44 lbs), the dose is based on weight: please enter ONLY the patient’s weight below (select imperial or metric units), and then click "Calculate".
- Calculator will display the appropriate minimum and maximum daily dose of Pheburane®.
For patients weighing equal to or more than 20 kg (44 lbs), the dose is based on Body Surface Area(BSA): please enter the patient’s height and weight below (select imperial or metric units), and then click "Calculate".
- Calculator will determine the patient’s Body Surface Area (BSA) using the Du Bois method*. Other methods can be used for calculating BSA.
- Calculator will then display the appropriate minimum and maximum daily doses of Pheburane®.
How to Take Pheburane®1,5
Pheburane® coated pellets can be taken 2 different ways with food consumption (meal or snack):
- Swallowed with a beverage – e.g., water, fruit juices, protein-free infant formulas.
- Sprinkled on soft food – apple sauce or carrot puree* – immediately before eating patients should swallow pellets immediately to minimize dissolution of coating.
* Administration of Pheburane® oral pellets with other foods has not been studied and is not recommended. Additionally, administration with soft food is only recommended in patients old enough to consume soft foods.
Patients should swallow pellets immediately (within 10 seconds) to minimize dissolution of coating.


The total daily dose of Pheburane® coated pellets should be administered in 3 to 6 divided amounts and taken with a meal or snack. Only use the calibrated dosing spoon provided with Pheburane® package to measure the dose. The maximum dosage is 20 grams per day.
Important Safety Information
Pheburane® is indicated as adjunctive therapy to standard of care, which includes dietary management, for the chronic management of adult and pediatric patients with urea cycle disorders (UCDs), involving deficiencies of carbamylphosphate synthetase (CPS), ornithine transcarbamylase (OTC) or argininosuccinic acid synthetase (AS).
Limitations of Use
Episodes of acute hyperammonemia may occur in patients while on Pheburane®. Pheburane® is not indicated for the treatment of acute hyperammonemia, which can be a life-threatening medical emergency that requires rapid acting interventions to reduce plasma ammonia levels. Read more
Important Safety Information
Pheburane® is indicated as adjunctive therapy to standard of care, which includes dietary management, for the chronic management of adult and pediatric patients with urea cycle disorders (UCDs).
Limitations of Use
Pheburane® is not indicated for the treatment of acute hyperammonemia. Read more
Important Safety Information
INDICATION
Pheburane® is indicated as adjunctive therapy to standard of care, which includes dietary management, for the chronic management of adult and pediatric patients with urea cycle disorders (UCDs), involving deficiencies of carbamylphosphate synthetase (CPS), ornithine transcarbamylase (OTC) or argininosuccinic acid synthetase (AS).
Limitations of Use
Episodes of acute hyperammonemia may occur in patients while on Pheburane®. Pheburane® is not indicated for the treatment of acute hyperammonemia, which can be a life-threatening medical emergency that requires rapid acting interventions to reduce plasma ammonia levels.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Neurotoxicity of Phenylacetate
Increased exposure to phenylacetate, the major metabolite of Pheburane®, may be associated with neurotoxicity in patients with UCDs. If symptoms of vomiting, nausea, headache, somnolence or confusion are present in the absence of high ammonia levels, consider reducing the dose of Pheburane®.
Hypokalemia
Renal excretion of phenylacetylglutamine may induce urinary loss of potassium. Monitor serum potassium during therapy, and initiate appropriate treatment when necessary.
Conditions Associated with Edema
In order to decide if administration of Pheburane® is appropriate in patients with diseases that involve edema, calculate the total amount of sodium patients will be exposed to, based on their weight or body surface area. If a patient develops new-onset edema or worsening edema while on treatment, discontinue administration of Pheburane® and initiate appropriate therapy.
Diabetes Mellitus, Hereditary Fructose Intolerance, Glucose-Galactose Malabsorption or Sucrase-Isomaltase Insufficiency
Avoid use of Pheburane® in patients with rare hereditary problems of fructose intolerance, glucose-galactose malabsorption or sucrose-isomaltase insufficiency.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common adverse reactions associated with the use of Pheburane® (incidence > 3%) are menstrual dysfunction, decreased appetite, body odor and bad taste or taste aversion.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
- Valproic acid, Haloperidol, or Corticosteroids: May increase plasma ammonia levels. Monitor ammonia levels closely.
- Probenicid: May inhibit renal excretion of metabolites of Pheburane® including phenylacetate and phenylacetylglutamine. Monitor patients for potential neurotoxicity.
OVERDOSAGE
Overdoses of Pheburane® exceeding ten-fold the maximum recommended dosage may produce emesis, CNS depression, metabolic acidosis with or without respiratory alkalosis, hypernatremia, hypokalemia, and hypophosphatemia. Symptoms of overdose overlap with those of acute hyperammonemia. If overdose occurs, discontinue Pheburane®, monitor plasma phenylacetate and ammonia levels closely, and institute appropriate emergency management.
To report suspected adverse reactions, contact Medunik USA at 1-844-884-5520 or [email protected].
Please read the Full Prescribing Information.References:
- Pheburane® (sodium phenylbutyrate) oral pellets [Prescribing Information]. Medunik USA, Inc.
- Kibleur Y, Dobbelaere D, Barth M, Brassier A, Guffon N. Results from a Nationwide Cohort Temporary Utilization Authorization (ATU) survey of patients in france treated with Pheburane® (Sodium Phenylbutyrate) taste-masked granules. Paediatr Drugs. 2014.
- Kibleur Y, Guffon N. Long-Term Follow-Up on a Cohort Temporary Utilization Authorization (ATU) Survey of Patients Treated with Pheburane (Sodium Phenylbutyrate) Taste-Masked Granules. Paediatr Drugs. 2016 Apr;18(2):139-44. doi: 10.1007/s40272-015-0159-8. PMID: 26747635.
- Guffon N, Kibleur Y, Copalu W, Tissen C, Breitkreutz J. Developing a new formulation of sodium phenylbutyrate. Arch Dis Child. 2012 Dec;97(12):1081-5. doi: 10.1136/archdischild-2012-302398. Epub 2012 Aug 31. PMID: 22941860.
- Peña-Quintana L, Llarena M, Reyes-Suárez D, Aldámiz-Echevarria L. Profile of sodium phenylbutyrate granules for the treatment of urea-cycle disorders: patient perspectives. Patient Prefer Adherence. 2017 Sep 6;11:1489-1496. doi: 10.2147/PPA.S136754. PMID: 28919721; PMCID: PMC5593420.
