PHEBURANE®P=PROVEN
Study Title: Results from a Nationwide Cohort Temporary Utilization Authorization (ATU) Survey of Patients in France Treated with Pheburane® (sodium phenylbutyrate) Taste-Masked Granules2†
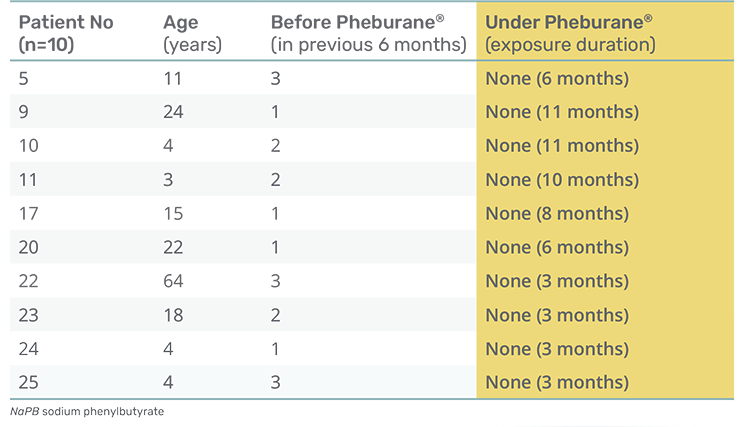
NO hyperammonemic episodes were experienced in the Pheburane® study treatment group (n=10).
- Additionally, patients who had not reported decompensations before Pheburane® treatment did not report any decompensations since starting Pheburane® treatment either (n=10).
Important Note: Episodes of acute hyperammonemia may occur in patients while on Pheburane®. Pheburane® is not indicated for the treatment of acute hyperammonemia, which can be a life-threatening medical emergency that requires rapid acting interventions to reduce plasma ammonia levels.
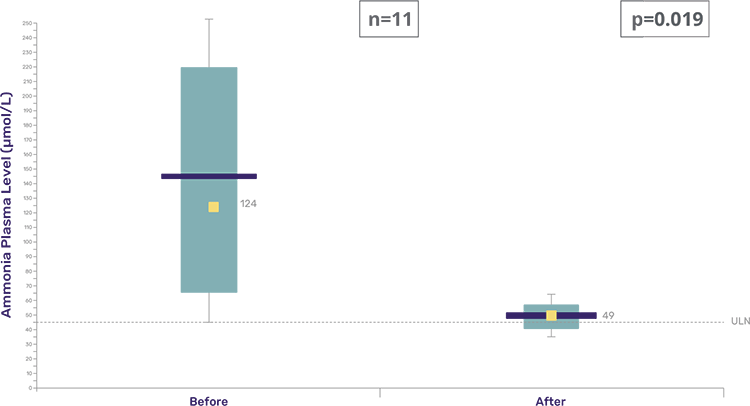
Pheburane® treatment led to significantly lower plasma ammonia (NH3) and glutamine (Gln) values compared to non-taste-masked NaPB treatments.2
- The median ranges (IQR) of plasma ammonia (NH3) went from 124 (68-221) during treatment with NaPB to 49 (39.5-54.5) during treatment with Pheburane® (p = 0.019).
- The median ranges (IQR) of glutamine (Gln) values went from 1,027 (905-1310) during treatment with NaPB to 845 (707-1075) during treatment with Pheburane® (p = 0.028).
Box-Whisker plots of maximal plasma ammonia values in the 6-month period before inclusion in the cohort ATU and then under Pheburane®
 * Based on temporary utilization authorization (ATU) protocol in France to analyze safety and efficacy in the treated cohort of patients with UCD.
* Based on temporary utilization authorization (ATU) protocol in France to analyze safety and efficacy in the treated cohort of patients with UCD.† The FDA-approved term pellets is used to describe Pheburane® in the United States. The term granules is used to describe Pheburane® in other countries.
Pheburane® greatly improved the tolerance and acceptability of NaPB.2
Study Quote: “Comparative data available from 9 UCD patients receiving doses of 2.5-10 g/day highlight a dramatic change in acceptability...”2
Subjects taking Pheburane® had lower incidence of vomiting and dysgeusia compared with non-taste-masked NaPB treatment, which impairs patients’ well-being and/or their acceptance/compliance with treatment.2
When on the non-taste-masked NaPB products and before the inclusion in the cohort ATU study, patients needed to have their NaPB treatment re-formulated into capsules (2/25 pts), through a nasogastric tube (4/25 pts) or gastrostomy (1/25). Pheburane® does not require tablets, syringes, or mixing.
Long-term Follow-up Study Design3
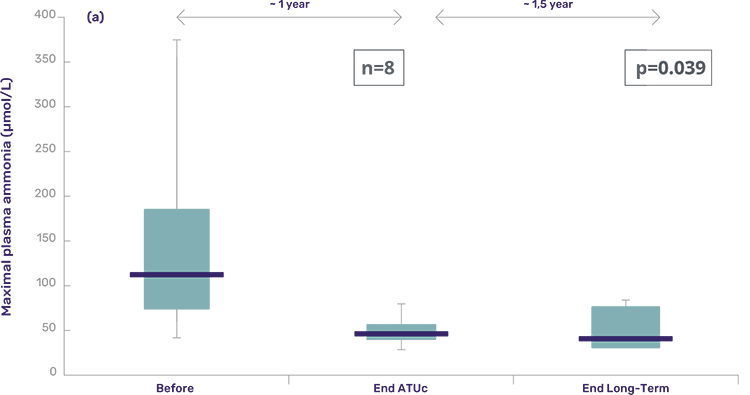
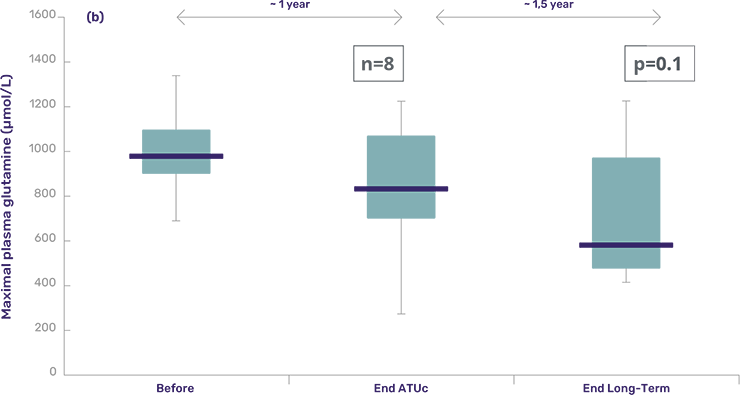
These patients are a subset of the ATU cohort, now followed for 2 years at the principal recruiting metabolic reference center. Of the 25 in the ATU cohort, 8 subjects were included in the follow-up. Almost all subjects had more than 1 year of treatment with Pheburane® – except for one subject that completed 8 months of treatment.
Pheburane® continued to demonstrate improved clinical status.3
- No episodes of decompensation were observed in the 8 subjects over a treatment period ranging from 8 to 30 months with Pheburane®.
- Ammonia and glutamine levels continued to improve and remained within normal range.
- No adverse events were reported with Pheburane® treatment in the long-term follow-up.
- Neurological examination was normal in all subjects and was either improved or stable since original admission to ATU cohort.
- Additionally, there was a dose increase in 4 subjects during the follow-up study, and subjects continued to use oral Pheburane® without needing an alternative route or device such as using a feeding tube or compounding the product.
Pheburane® is for oral administration only. Administration via gastrostomy or nasogastric tubes has not been evaluated.
Box-Whisker plot statistics of maximal plasma ammonia values
Box-Whisker plot statistics of maximal plasma glutamine values
 Figures on this page are adapted from Kibleur Y, Guffon N. Long-Term Follow-Up on a Cohort Temporary Utilization Authorization (ATU) Survey of Patients Treated with Pheburane® (Sodium Phenylbutyrate) Taste-Masked Granules. Paediatr Drugs. 2016 Apr;18(2):139-44. doi:10.1007/s40272-015-0159-8. PMID: 26747635.
Figures on this page are adapted from Kibleur Y, Guffon N. Long-Term Follow-Up on a Cohort Temporary Utilization Authorization (ATU) Survey of Patients Treated with Pheburane® (Sodium Phenylbutyrate) Taste-Masked Granules. Paediatr Drugs. 2016 Apr;18(2):139-44. doi:10.1007/s40272-015-0159-8. PMID: 26747635.Important Safety Information
Pheburane® is indicated as adjunctive therapy to standard of care, which includes dietary management, for the chronic management of adult and pediatric patients with urea cycle disorders (UCDs), involving deficiencies of carbamylphosphate synthetase (CPS), ornithine transcarbamylase (OTC) or argininosuccinic acid synthetase (AS).
Limitations of Use
Episodes of acute hyperammonemia may occur in patients while on Pheburane®. Pheburane® is not indicated for the treatment of acute hyperammonemia, which can be a life-threatening medical emergency that requires rapid acting interventions to reduce plasma ammonia levels. Read more
Important Safety Information
Pheburane® is indicated as adjunctive therapy to standard of care, which includes dietary management, for the chronic management of adult and pediatric patients with urea cycle disorders (UCDs).
Limitations of Use
Pheburane® is not indicated for the treatment of acute hyperammonemia. Read more
Important Safety Information
INDICATION
Pheburane® is indicated as adjunctive therapy to standard of care, which includes dietary management, for the chronic management of adult and pediatric patients with urea cycle disorders (UCDs), involving deficiencies of carbamylphosphate synthetase (CPS), ornithine transcarbamylase (OTC) or argininosuccinic acid synthetase (AS).
Limitations of Use
Episodes of acute hyperammonemia may occur in patients while on Pheburane®. Pheburane® is not indicated for the treatment of acute hyperammonemia, which can be a life-threatening medical emergency that requires rapid acting interventions to reduce plasma ammonia levels.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Neurotoxicity of Phenylacetate
Increased exposure to phenylacetate, the major metabolite of Pheburane®, may be associated with neurotoxicity in patients with UCDs. If symptoms of vomiting, nausea, headache, somnolence or confusion are present in the absence of high ammonia levels, consider reducing the dose of Pheburane®.
Hypokalemia
Renal excretion of phenylacetylglutamine may induce urinary loss of potassium. Monitor serum potassium during therapy, and initiate appropriate treatment when necessary.
Conditions Associated with Edema
In order to decide if administration of Pheburane® is appropriate in patients with diseases that involve edema, calculate the total amount of sodium patients will be exposed to, based on their weight or body surface area. If a patient develops new-onset edema or worsening edema while on treatment, discontinue administration of Pheburane® and initiate appropriate therapy.
Diabetes Mellitus, Hereditary Fructose Intolerance, Glucose-Galactose Malabsorption or Sucrase-Isomaltase Insufficiency
Avoid use of Pheburane® in patients with rare hereditary problems of fructose intolerance, glucose-galactose malabsorption or sucrose-isomaltase insufficiency.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common adverse reactions associated with the use of Pheburane® (incidence > 3%) are menstrual dysfunction, decreased appetite, body odor and bad taste or taste aversion.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
- Valproic acid, Haloperidol, or Corticosteroids: May increase plasma ammonia levels. Monitor ammonia levels closely.
- Probenicid: May inhibit renal excretion of metabolites of Pheburane® including phenylacetate and phenylacetylglutamine. Monitor patients for potential neurotoxicity.
OVERDOSAGE
Overdoses of Pheburane® exceeding ten-fold the maximum recommended dosage may produce emesis, CNS depression, metabolic acidosis with or without respiratory alkalosis, hypernatremia, hypokalemia, and hypophosphatemia. Symptoms of overdose overlap with those of acute hyperammonemia. If overdose occurs, discontinue Pheburane®, monitor plasma phenylacetate and ammonia levels closely, and institute appropriate emergency management.
To report suspected adverse reactions, contact Medunik USA at 1-844-884-5520 or [email protected].
Please read the Full Prescribing Information.References:
- Pheburane® (sodium phenylbutyrate) oral pellets [Prescribing Information]. Medunik USA, Inc.
- Kibleur Y, Dobbelaere D, Barth M, Brassier A, Guffon N. Results from a Nationwide Cohort Temporary Utilization Authorization (ATU) survey of patients in france treated with Pheburane® (Sodium Phenylbutyrate) taste-masked granules. Paediatr Drugs. 2014.
- Kibleur Y, Guffon N. Long-Term Follow-Up on a Cohort Temporary Utilization Authorization (ATU) Survey of Patients Treated with Pheburane (Sodium Phenylbutyrate) Taste-Masked Granules. Paediatr Drugs. 2016 Apr;18(2):139-44. doi: 10.1007/s40272-015-0159-8. PMID: 26747635.
- Guffon N, Kibleur Y, Copalu W, Tissen C, Breitkreutz J. Developing a new formulation of sodium phenylbutyrate. Arch Dis Child. 2012 Dec;97(12):1081-5. doi: 10.1136/archdischild-2012-302398. Epub 2012 Aug 31. PMID: 22941860.
- Peña-Quintana L, Llarena M, Reyes-Suárez D, Aldámiz-Echevarria L. Profile of sodium phenylbutyrate granules for the treatment of urea-cycle disorders: patient perspectives. Patient Prefer Adherence. 2017 Sep 6;11:1489-1496. doi: 10.2147/PPA.S136754. PMID: 28919721; PMCID: PMC5593420.
